In today's IOT (Internet Of Things) world there are various wearable/Portable smart devices coming up in the market which are battery operated. These devices also need to be Power efficient such that it can run on battery for a long time. And here the concept of Low Power Design comes into existence.
Different types of strategies used to reduce power consumption. Some of them are listed below.
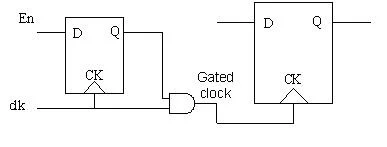
1. Clock Gating
Clock being the highest frequency toggling signal contributes maximum towards the dynamic power consumption in the SoC even when the flops that are being fed by the clock are not changing their state. So, it is practical to gate the clock from reaching the set of registers or maybe some block in the design. This will ensure that there is no switching activity due to change in the clock and hence reduction in dynamic power consumption.
2. Power gating
Power gating is a technique to shut down the power of a block when it is not required to be On. i.e In Mobile voice processing block can be shut down when the user is not having an incoming or outgoing call. This is the best method of reducing power consumption.
3. Multiple Vt Library cells
Nowadays the user provides the same cells with two different threshold voltage in the library. So that synthesis tools can choose cells depending on the requirement. With low Vt, sub-threshold leakage will increase but speed will also be higher. So for timing critical path synthesis tool will insert low Vt cells and at another path high Vt cell.
4. Dynamic voltage and frequency scaling
Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS) describes the use of two power saving techniques (dynamic frequency scaling and dynamic voltage scaling). In this technique same block can be working at the different voltage at the different time .i.e some time it is required to do high computation (complex equation solver) task then it needs more speed so it can operate at high voltage. While some time low computation is required so it can operate at a lower voltage.
5. Supply voltage reduction
As power is directly proportional to voltage (p =iv), with a reduction in voltage, power consumption will reduce. But again with a reduction in voltage will reduce switching speed as well.
6. Multi-voltage design
In SOC some block ( RAM) are such which require higher speed, so that block can be powered with higher voltage. While some block (Peripheral device) which does not needs high speed so that block can be powered with lower voltage, which in turn can reduce leakage power. In earlier days people used to have the same voltage for the whole design which makes it necessary to operate at high voltage. While this new technique, we can achieve leakage reduction.
In upcoming posts, we will discuss more on UPF(Unified Power Format) and low power verification.